Getting Started
The Compose UI Components library includes pre-built Jetpack Compose components that let you easily load and display data from the Stream Chat API, without much code.
Not using Compose yet? Check out our XML-based UI Components.
| Channels Screen (Light Theme) | Messages Screen (Light Theme) |
|---|---|
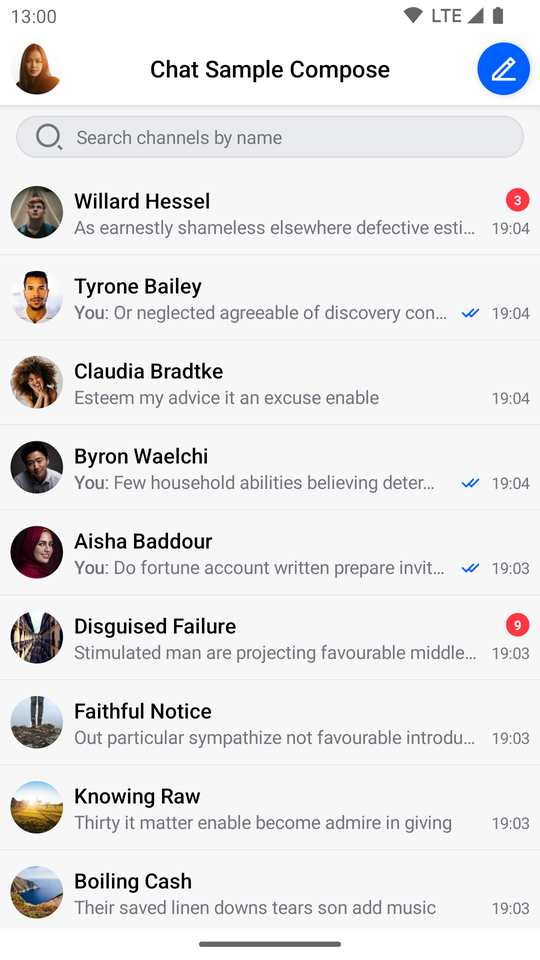 | 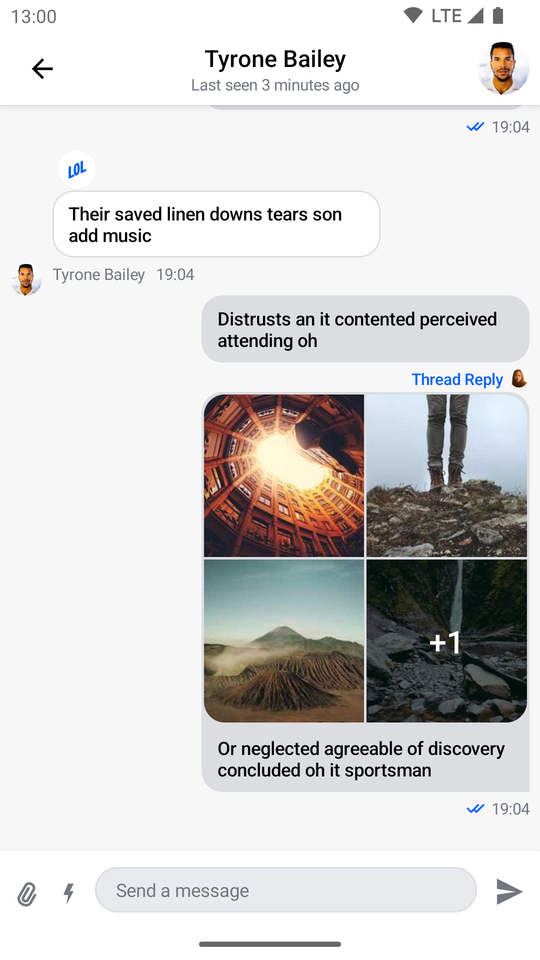 |
| Channels Screen (Dark Theme) | Messages Screen (Dark Theme) |
|---|---|
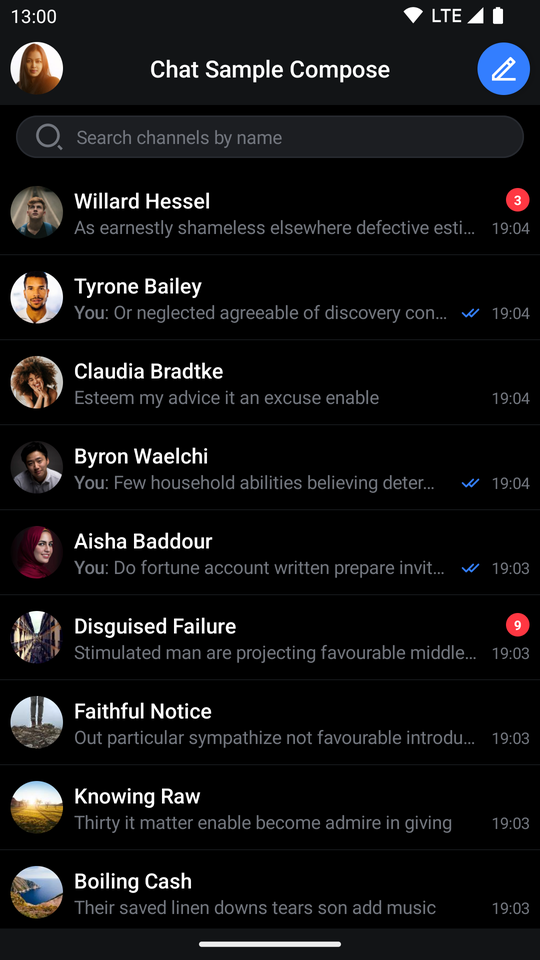 | 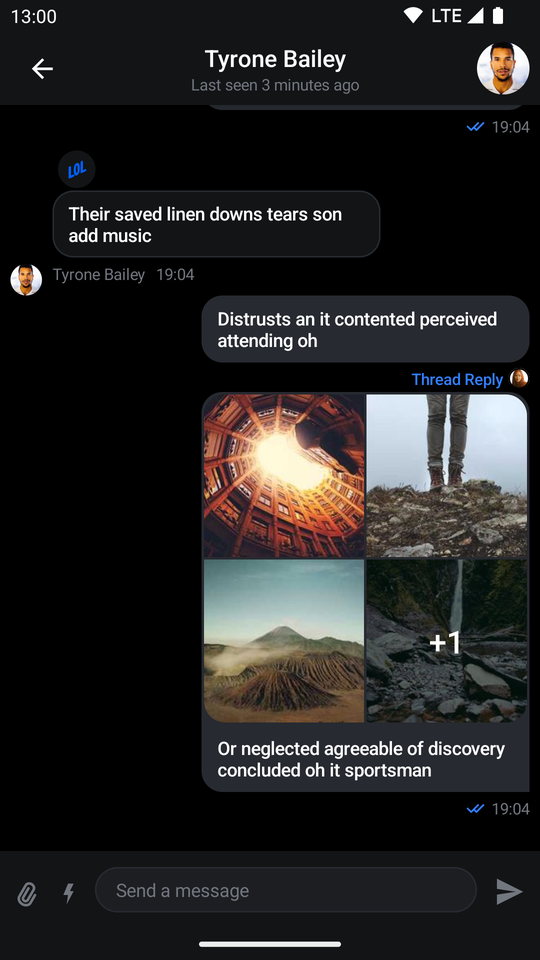 |
This library builds on top of the offline library and provides three types of components:
- Screen components: Fully built screens that work out-of-the-box, but offer much more limited customization.
- Bound components: Fully built components that represent a part of the screen and are bound to
ViewModelsthat we provide, for business logic, events, and state handling. These provide extensive behavior and UI customization. - Stateless components: Simple components that rely on external state and know nothing about our
ViewModels. Fully customizable.
The sample app showcases the Compose UI Components in action.
See the individual pages for these components to learn more about them.
Channel components:
Message components:
- Messages Screen
- Message List Header
- Message List
- Message Composer
- Attachments Picker
- Selected Message Menu
- Reactions
Utility components
Checklist
For a successful integration of our Compose UI Components, follow these steps:
- Set up your project to work with Jetpack Compose, as per the official documentation.
- Dependency. Add the dependency to your app, as described on the Dependencies page.
- Set up the
ChatClient. Learn how to set up the ChatClient here. - User connection. Read how to handle the user connection here and info about User Tokens here.
- State and Offline. Using the
StatePluginis mandatory if you want to use our UI Components. Read the State Overview page for more information. Also, it's a good idea to add offline support for better UX.
If you're looking to explore the setup and our components in a step-by-step way, check out our Compose In-App Messaging Tutorial. Also, check-out our sample app.
ViewModels
Our bound components require a ViewModel to connect to for state and event handling. Some of our components build the ViewModel by default, but you'll likely want to build your own instances to gain more control over their lifecycle.
These are Jetpack ViewModels, so they allow the components to retain data across configuration changes. It's your responsibility to create these in the correct scope, usually in a Fragment or Activity.
For example, if you want to add the MessageList component to your UI, you can do it like so:
// 1
val factory by lazy {
MessagesViewModelFactory(
context = this,
chatClient = ChatClient.instance(),
channelId = "messaging:123",
enforceUniqueReactions = true,
messageLimit = 30
)
}
// 2
val listViewModel: MessageListViewModel by viewModels { factory }
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
// 3
setContent {
ChatTheme {
MessageList(
modifier = Modifier
.padding(8.dp)
.fillMaxSize(),
viewModel = listViewModel // 4
)
}
}
}
- Create the
ViewModelfactory, providing any necessary parameters. - Build the
ViewModel, using the AndroidViewModelAPIs and thefactoryyou created. - Set the content of your
ActivityorFragmentand call theMessageListcomponent. - Pass in the
ViewModelto the component.
By passing in the ViewModel, the component knows where to fetch the data from and where to delegate various events, like selecting a message or tapping on a thread reply.
You can learn more about each component's setup and usages on their individual pages.
Sample App
The Compose UI Components sample app is an open-source and fully functional messaging application that lets you explore and test our API. It features channels, threads, reactions, various attachments, UI updates and offline storage.
All built using our Compose UI Components and the offline library.
Customization
Our Compose UI Components offer different ways of customization:
- Behavior: Through event handlers for clicks, taps, dismiss requests and more.
- Appearance: Through different parameters for shapes, colors or a Compose
Modifier, you can customize the component appearance. - Content: Some components provide slot APIs, composable function parameters that let you define (or override) their internal content.
- Design style: By using our
ChatThemecomponent as the root of all of your UI, you can define the colors, typography, shapes, attachment factories, reaction types and various other things our components use. Through this, you can apply your own design style to all Compose UI Components.
To learn what level of customization each component exposes, check out their respective documentation pages. If you want to learn about general customization, read our ChatTheme page.